What is the DHS 38 form?
The DHS 38 form is a document used by the Michigan Department of Human Services. It's designed to collect information from employers regarding an employee's work and income. This information might be needed for various purposes, such as verifying employment or calculating benefits.
Who needs to fill out the DHS 38 form?
Employers are required to fill out the DHS 38 form when requested by the Michigan Department of Human Services. This request can stem from an inquiry or investigation related to employee benefits or assistance programs.
What information is required on the DHS 38 form?
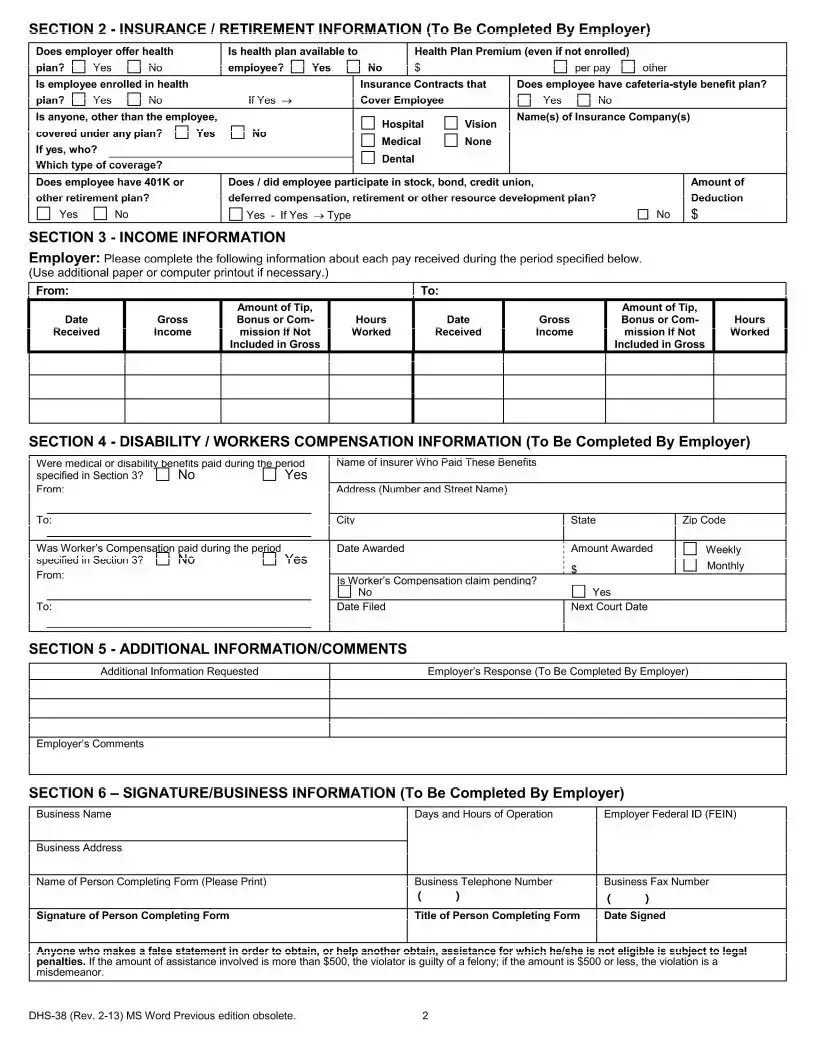
The form requires detailed employment information including employment status, occupation, wages, tips or bonuses, insurance, retirement plans, and any disability or worker's compensation paid. Employers also need to verify the employee's start date, pay schedule, and other employment conditions.
Is there a penalty for not completing the DHS 38 form?
Yes, there is a penalty for failing to complete the DHS 38 form. The document warns that failure to provide the requested information could result in the issuance of a subpoena.
Can student employment information be released without consent?
No, according to the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA), employment information for students cannot be released without written authorization from the student. The DHS 38 form includes a section for student employees aged 18 or older to sign, authorizing the release of their employment information.
What should I do if I don't understand the form?
If you have questions or need assistance with the DHS 38 form, you are advised to contact a Department of Human Services office in your area. DHS employees can help clarify what is required without providing legal advice.
How does the DHS handle discrimination?
The Department of Human Services states that it will not discriminate against any individual or group based on race, religion, age, and several other criteria. Should you need assistance due to disabilities under the Americans with Disabilities Act, you are encouraged to make your needs known to a local DHS office.
What is the return process for the DHS 38 form?
Employers are instructed to fill out the form and return it to the specific specialist and address noted on the form by the specified return date. An envelope is usually provided for this purpose.
Is completion of the DHS 38 form mandatory?
Yes, completing the form is required when requested by the Department of Human Services. Required information includes details about employment, income, and benefits that are relevant to DHS inquiries or investigations.
What happens if false information is provided on the DHS 38 form?
Anyone found to be providing false information on the DHS 38 form, either to obtain assistance fraudulently or to help another obtain assistance, is subject to legal penalties. The seriousness of the penalty depends on the amount of assistance involved, distinguishing between felony and misdemeanor violations.