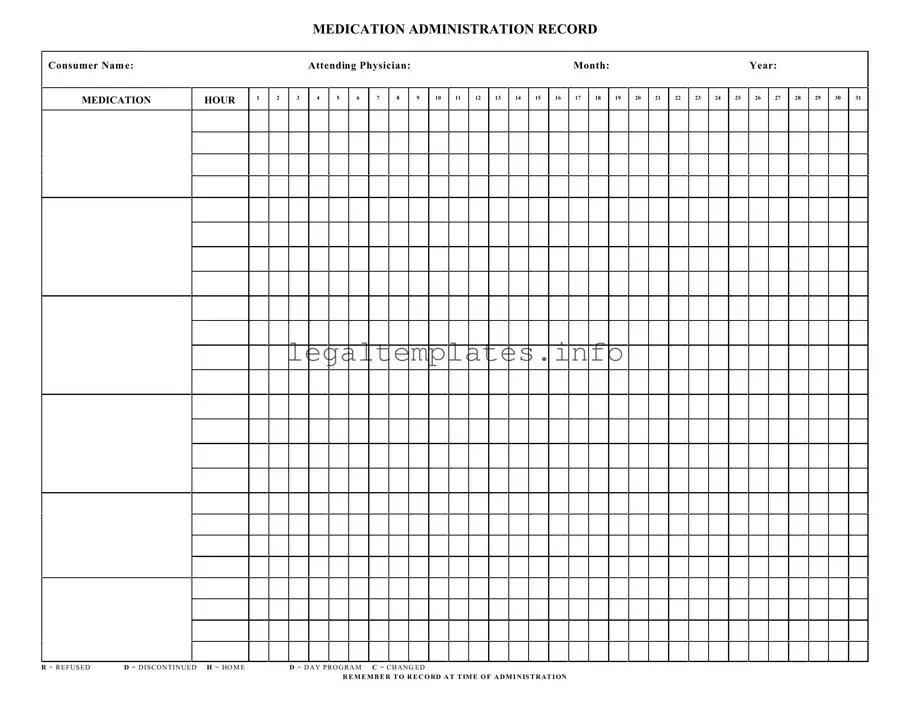
What is a Medication Administration Record Sheet (MAR)?
A Medication Administration Record Sheet, commonly referred to as an MAR, is a comprehensive report that tracks all the medication prescribed and administered to a patient over a period. It includes detailed information on the dosage, timing, and frequency of medication intake. This form is crucial in ensuring patients receive their medications correctly and safely, serving as a communication tool among healthcare providers.
Who needs to fill out the MAR?
Healthcare professionals such as nurses or caregivers who administer medications are primarily responsible for filling out the MAR. It's their duty to accurately record each instance of medication administration, including the time and any deviations from the prescribed regimen, like a missed dose or a patient refusal.
What do the abbreviations on the MAR mean (R, D, H, C)?
The abbreviations found on the MAR are critical for noting specific circumstances regarding medication administration. "R" stands for refused, indicating that a patient did not take a scheduled dose. "D" means discontinued, showing that the medication has been stopped. "H" signifies that the patient was at home, possibly explaining a missed dose in a care facility context. Lastly, "C" denotes a change in the medication, dosage, or timing.
Why is it important to record medication administration at the time of administration?
Recording medication administration at the time it occurs is vital for maintaining an accurate account of a patient's medication management. This real-time documentation helps prevent errors, such as double dosing or skipping a medication, ensuring the patient's safety. It also provides a clear record for any subsequent caregiver or healthcare provider that may be involved in the patient’s care.
Can modifications be made to the MAR?
Yes, modifications can be made to the MAR to reflect changes in a patient's medication regimen, such as dosage adjustments or new prescriptions. However, any changes should be made carefully and clearly, with the prior entry remaining legible. This ensures the continuity and accuracy of the medication record. Typically, any modifications should be verified and initialed by a healthcare professional.
What should be done if a medication error occurs?
In the event of a medication error, it's crucial to take immediate action to ensure the patient's safety. The error should be documented in the MAR, including what occurred and the steps taken afterward. Reporting the incident to the appropriate supervisor or healthcare provider for further assessment and response is also necessary. Learning from these incidents can help prevent future errors.
How long should MAR records be kept?
The retention period for MAR records varies depending on regulations and guidelines, which may differ by jurisdiction and type of healthcare facility. Generally, it's advised to keep these records for a significant period after the patient’s last entry to ensure that they can be referenced if there are questions about the patient’s medication history or any related legal matters. Consulting with facility policy or legal counsel can provide specific guidance.
What role does the MAR play in patient care?
The MAR plays a pivotal role in patient care by serving as a detailed ledger of a patient’s medication management. It aids in ensuring accuracy in medication administration, promoting patient safety, and facilitating clear communication among the healthcare team. The MAR also supports regulatory compliance and helps in the audit process by providing a clear history of medication administration practices.