What is a Negative HIV Test result?
A Negative or Non-Reactive HIV Test result means that no HIV antibodies were detected in the person's blood at the time of the test. It's important to note that there is a "window period" during which the body may not have produced enough antibodies for the test to detect, even if the person has been infected with HIV.
What should I do after receiving a Negative HIV Test result?
After receiving a Negative HIV Test result, it's recommended to continue practicing safe behaviors to prevent HIV infection. Depending on personal risk factors, follow-up testing might be advised, as antibodies may take time to develop after exposure to the virus. It's also a good opportunity to discuss with a healthcare provider any concerns or questions about HIV prevention.
Is a follow-up appointment necessary after a Negative HIV Test result?
Whether a follow-up appointment is necessary depends on individual risk factors and the timing of the last potential exposure. The form references a section for scheduling a follow-up appointment, indicating its importance in certain cases, such as if the test was taken during the window period.
What does the "window period" mean?
The "window period" refers to the time immediately after infection during which HIV antibodies have not yet reached detectable levels. During this period, a person might test negative for HIV even if they are infected. The length of the window period can vary, but it is generally between 2 to 8 weeks.
Can I trust a Negative HIV Test result?
A Negative HIV Test result is reliable for exposures that occurred more than the window period ago. If there has been a recent potential exposure, it's possible for the test to not detect the infection. Discussing personal risk factors with a healthcare provider can provide guidance on whether re-testing is recommended.
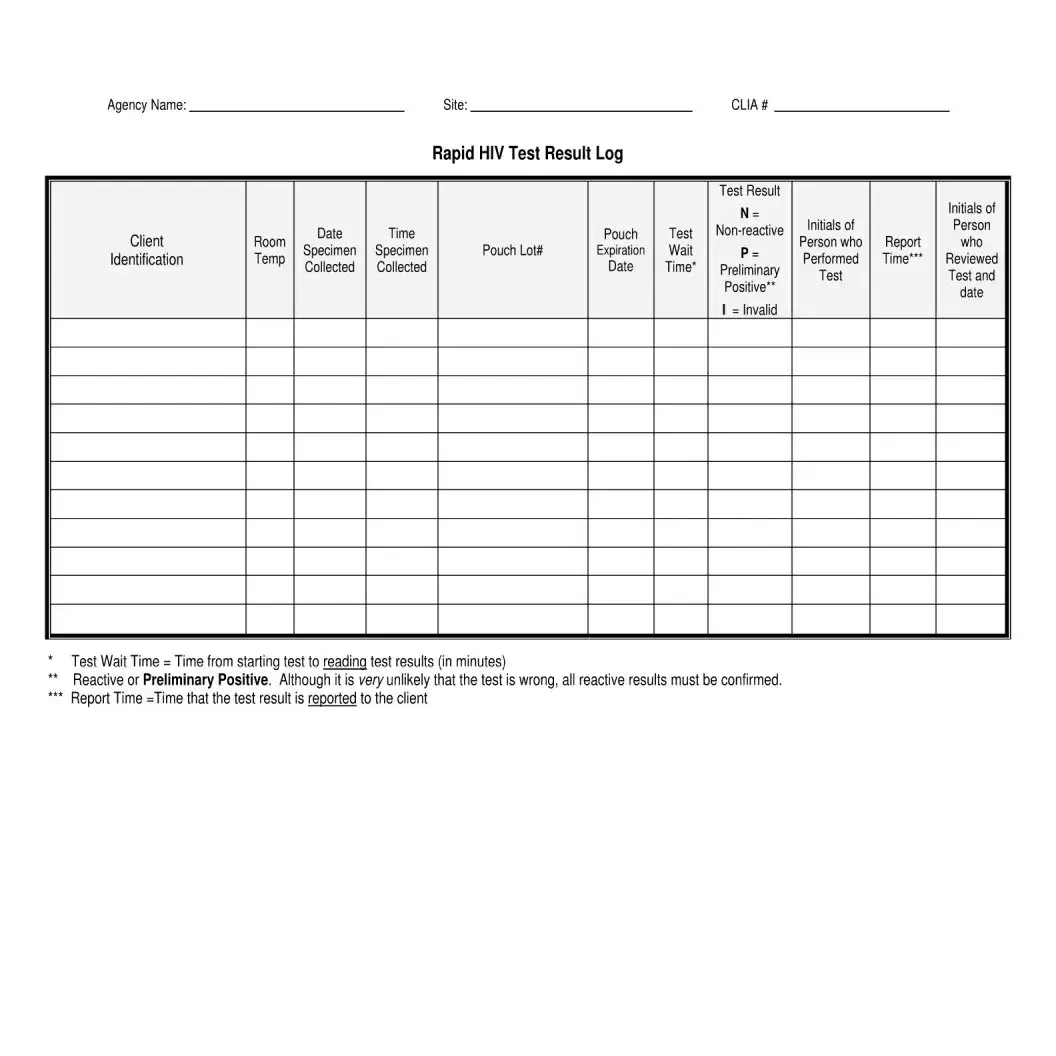
What happens if my HIV test result is initially reactive?
If an HIV test result is initially reactive, it indicates a possible presence of HIV antibodies. However, confirmatory testing is required to establish a diagnosis of HIV. An initial reactive result needs to be followed by additional, more specific tests.
Why is the Client Signature required on the form?
The Client Signature on the form is a way to confirm that the individual has received the information about their test result and understands the next steps, whether the result is negative, positive, or requires further testing. It's also part of the procedural documentation for the agency providing the test.
What is the Counselor Signature for on the form?
The Counselor Signature confirms that the test result has been communicated to the client and that any necessary counseling or referral for additional services has been provided. It ensures accountability and records that proper procedures have been followed.
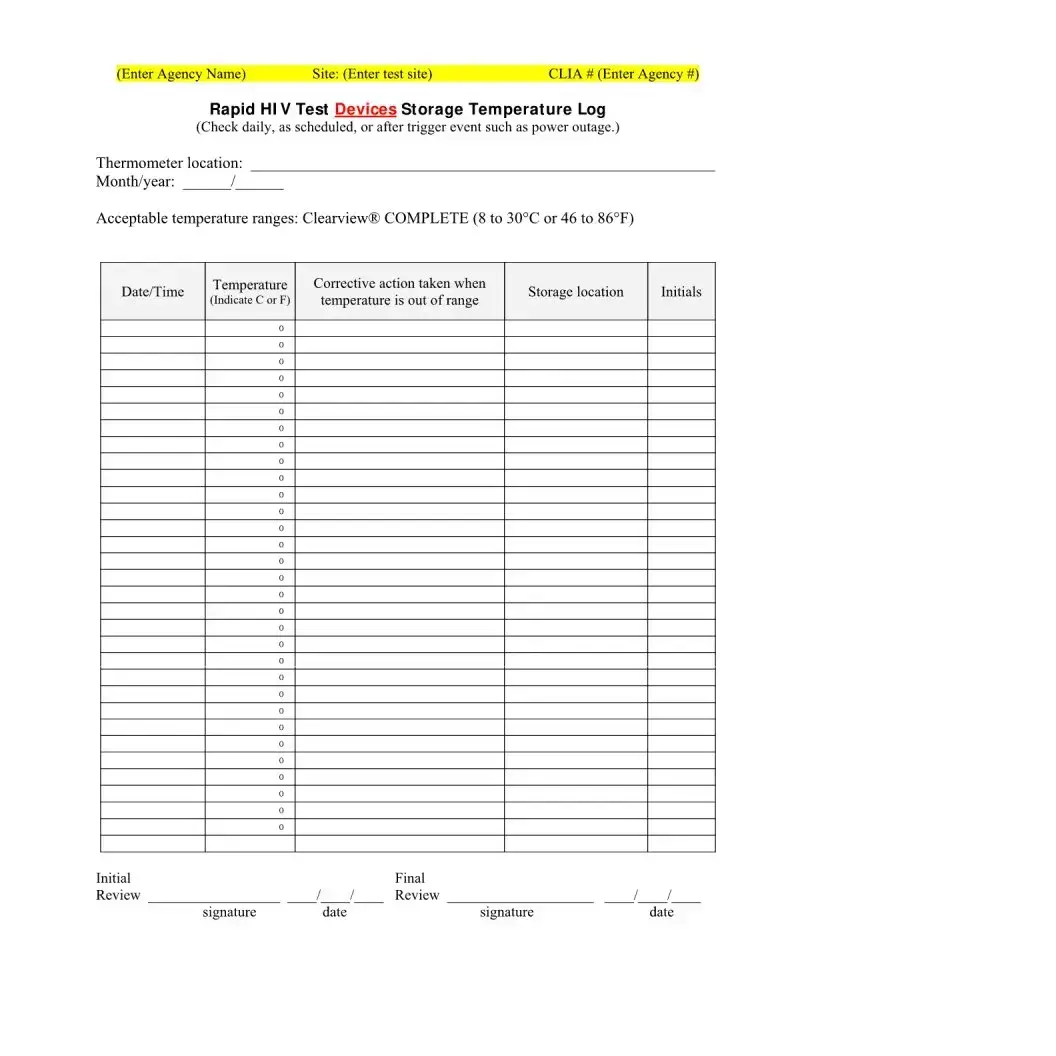
What does the storage temperature log indicate?
The storage temperature log is vital for ensuring that the test kits are stored within their required temperature range to maintain accuracy. It records daily temperatures, any deviations, and actions taken to correct them, safeguarding the reliability of future tests.
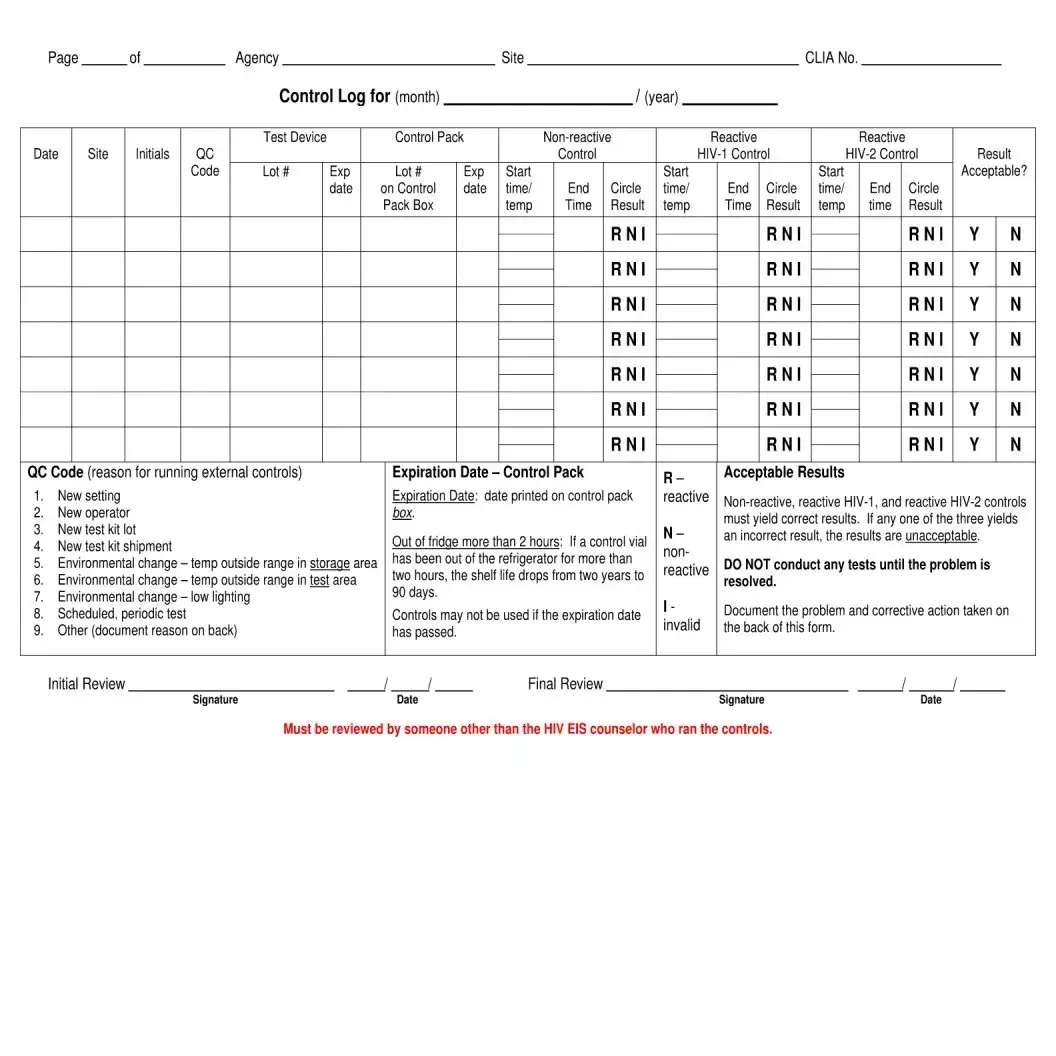
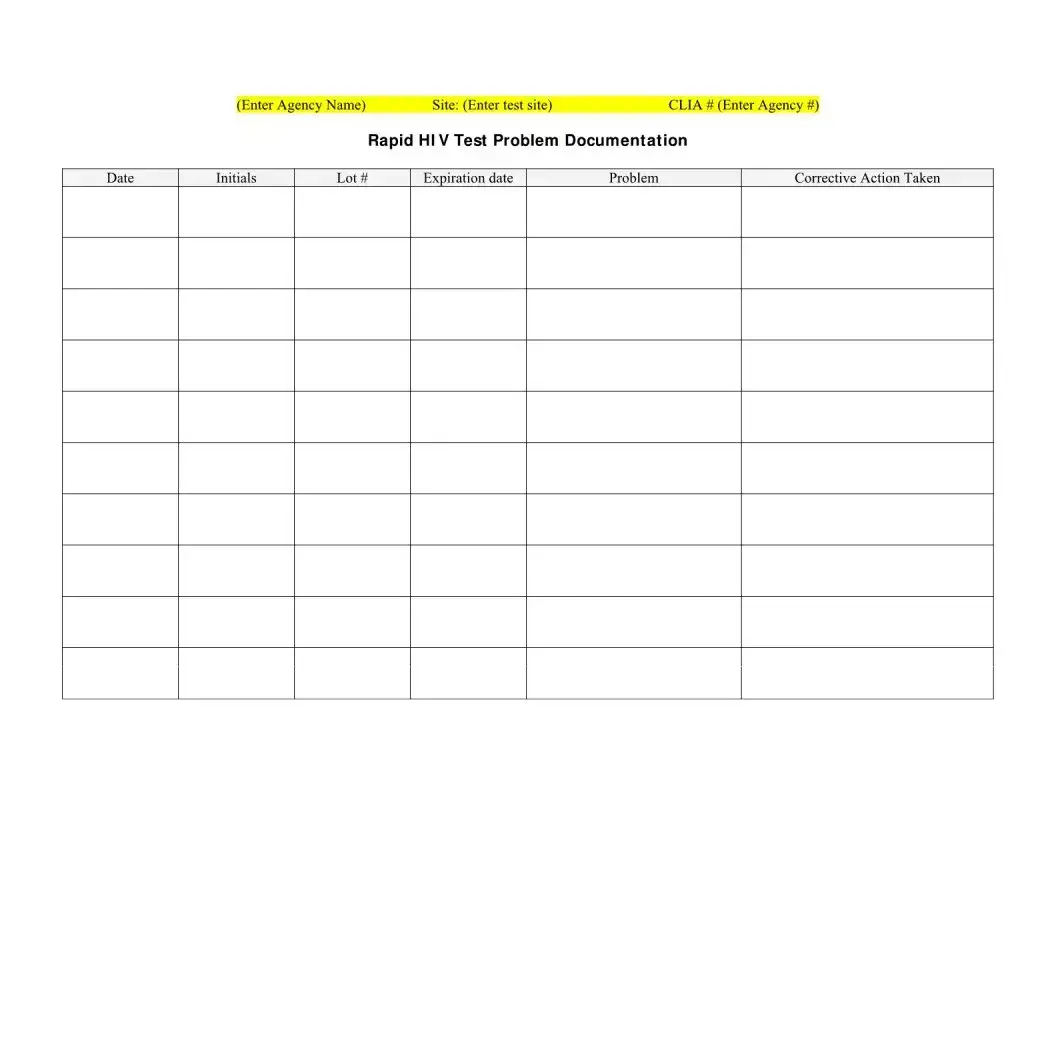
What if the Rapid HIV Test Devices are stored out of the recommended temperature range?
If the Rapid HIV Test Devices are stored out of the recommended temperature range, it can affect the integrity and accuracy of the tests. The corrective actions taken, as recorded in the temperature log, are crucial for addressing any potential impact on test results. Additional measures might include verifying the accuracy of affected tests or discarding compromised test kits.